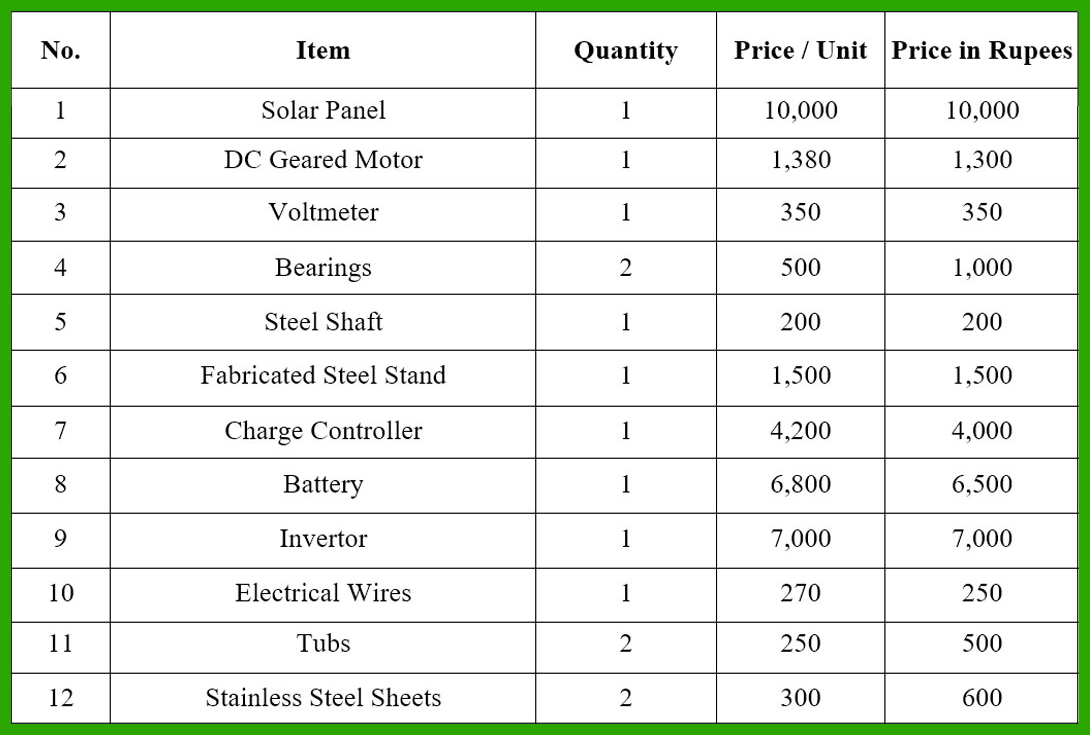
LIST OF COMPONENTS
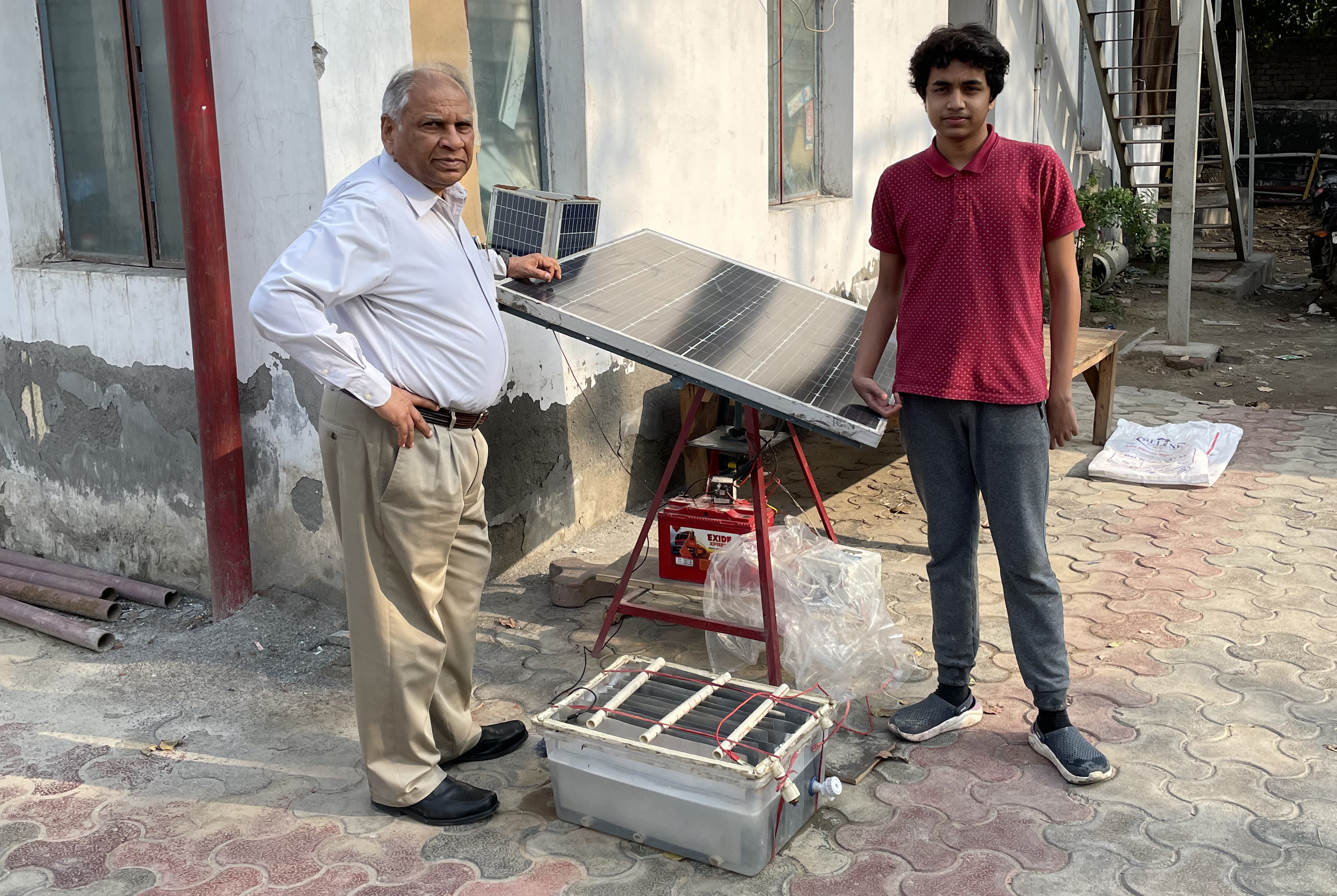

The mechanism of the Solar-Powered Water Purifier involves the use of stainless sheets in the chlor-alkali process, specifically the electrolysis of NaCl (sodium chloride). This process occurs through two key components: the cathode and the anode.
The cathode, typically made of stainless serves as the negative electrode. When an electric current passes through the purifier, the cathode attracts positively charged ions. In this case, the current promotes the reduction of sodium ions (Na+) present in the NaCl solution. As a result, sodium ions gain electrons and are converted into sodium metal (Na), which collects at the cathode. On the other hand, the anode, acts as the positive electrode. Here, the current promotes the oxidation of chloride ions (Cl-) found in the NaCl solution. The chloride ions lose electrons and are converted into chlorine gas (Cl2) at the anode.
Overall, the electrolysis of NaCl leads to the separation of sodium and chlorine components. The sodium metal obtained at the cathode can be utilized for various purposes, while the chlorine gas released at the anode can be safely captured or disposed of. This process allows for the purification of water, effectively removing impurities and contaminants.
To ensure the quality of the purified water, I measured the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) and pH levels of both the incoming water and the outgoing water from the tank. This system helps assess the effectiveness of the purification process and ensures that the water meets the desired standards. For checking the TDS, a TDS meter or conductivity meter is utilized. The meter measures the electrical conductivity of the water, which is directly related to the concentration of dissolved solids. This provides an indication of the level of dissolved minerals, salts, and other impurities present in the water before and after the purification process. Similarly, the pH of the water is measured using a pH meter or pH test strips. The strips are dipped into the tank to assess the acidity or alkalinity of the water. The pH value determines whether the water is within the acceptable range, as extreme pH levels can be detrimental to health.
The solar-powered water purifier holds immense utility in addressing the critical need for clean and drinkable water. Its utility extends to various sectors, making it a versatile solution for multiple applications. In agriculture, it can be utilized for irrigation purposes, ensuring that crops receive clean and uncontaminated water, in turn leading to improved yields and healthier produce. The purifier also provides clean drinkable water in remote communities where access is limited. Its portable design and using renewable solar energy makes it suitable for disaster stricken areas, enabling rapid deployment and immediate access to purified water.
The future scope of my project is vast and promising. With increasing concerns about water scarcity and the need for sustainable solutions, my innovative technology has the potential to revolutionize access to clean and safe water not only in remote villages in Delhi but other parts of India. By continuously refining its mechanism and expanding its outreach through strategic partnerships and collaborations, I envision a future where every individual will have a reliable water source, fostering improved health and well-being.

